Biotechnology in agriculture involves using scientific techniques to modify plants and animals to enhance productivity and resistance to diseases. It plays a crucial role in improving crop yields and food security.
Biotechnology leverages genetic engineering, molecular markers, and tissue culture to create robust agricultural practices. Farmers benefit from crops that resist pests, diseases, and extreme weather conditions. These advancements reduce reliance on chemical pesticides and fertilizers, promoting a more sustainable environment.
Enhanced nutritional content in genetically modified crops addresses malnutrition issues globally. Additionally, biotechnology enables faster and more precise breeding techniques. This modern approach helps meet the growing food demands of an increasing population while ensuring environmental sustainability. The integration of biotechnology in agriculture is essential for future food security and environmental health.
The Fusion Of Biotechnology And Agriculture
The fusion of biotechnology and agriculture is transforming farming practices worldwide. This synergy brings innovative solutions to age-old problems. Through biotechnology, agriculture now benefits from enhanced crop yields and sustainable practices.
Agricultural Evolution
Agriculture has evolved significantly over the centuries. Traditional farming relied on natural methods and manual labor. The introduction of machinery revolutionized farming in the 20th century. Today, biotechnology is the driving force behind agricultural progress.
Modern biotechnology enables precise genetic modifications. This allows farmers to grow crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases. Biotechnology also helps in improving nutritional content in crops. Below is a comparison of traditional and modern agricultural practices:
| Aspect | Traditional Agriculture | Modern Biotechnology |
|---|---|---|
| Pest Control | Manual methods, pesticides | Genetically modified pest-resistant crops |
| Yield | Variable, often low | Consistently high yields |
| Nutritional Value | Basic nutritional content | Enhanced nutritional value |
Modern Biotech Applications
Modern biotechnology has a wide range of applications in agriculture. These applications improve efficiency and sustainability. Some key applications include:
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs): Crops are modified for better traits.
- CRISPR Technology: This allows precise editing of crop genes.
- Bio-fertilizers: Natural fertilizers improve soil health.
- Bio-pesticides: These control pests without harming the environment.
- Plant Tissue Culture: This helps in rapid multiplication of plants.
These applications enhance the resilience of crops. They also reduce dependency on chemical inputs. Farmers benefit from increased productivity and reduced costs.
Biotechnology in agriculture is not just about improving crops. It also focuses on sustainable practices. This ensures that future generations can continue to benefit from these advancements. The fusion of biotechnology and agriculture promises a brighter and more sustainable future for farming.
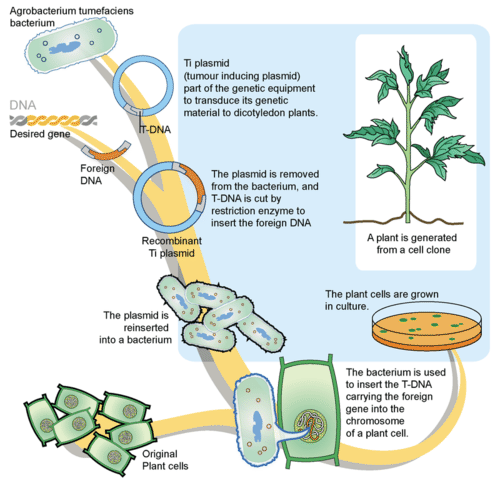
Credit: www.ck12.org
Genetic Engineering: Tailoring Crop Traits
Genetic engineering plays a significant role in modern agriculture. It helps modify crop traits for better yield. Scientists use this technology to introduce new traits in plants. These traits can make crops more resilient and productive.
Herbicide Tolerance
Herbicide tolerance is a crucial trait in engineered crops. Farmers use herbicides to control weeds. Weeds compete with crops for nutrients and water. Herbicide-tolerant crops can survive these chemicals.
This means farmers can use herbicides without harming the crops. It makes weed control more effective and less labor-intensive.
| Herbicide | Crops | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Glyphosate | Soybean, Corn | Effective Weed Control |
| Glufosinate | Canola, Cotton | Improved Crop Yield |
Disease Resistance
Disease resistance is another vital trait. Crops often suffer from various diseases. These diseases reduce yield and quality. Genetic engineering helps develop disease-resistant crops.
Scientists introduce genes that help plants fight diseases. This makes crops healthier and more productive. It also reduces the need for chemical pesticides.
- Tomato plants resist viral infections.
- Potato plants fight fungal diseases.
- Papaya resists the Papaya Ringspot Virus.
Disease-resistant crops are a game-changer. They ensure food security and reduce farming costs.
Biotech Crops On The Market
Biotechnology has transformed agriculture. Biotech crops bring many benefits. Farmers grow these crops for better yield and pest resistance. Let’s explore some key biotech crops on the market.
Soybeans
Soybeans are a major biotech crop. Farmers love them for their high protein content. Biotech soybeans resist pests and herbicides. This makes farming easier and more efficient. Also, these soybeans need fewer chemicals, which is better for the environment.
| Benefits | Details |
|---|---|
| Herbicide Resistance | Allows farmers to control weeds easily. |
| Pest Resistance | Reduces the need for pesticides. |
| Higher Yield | Increases the amount of soybeans produced. |
Corn
Corn is another important biotech crop. It is used in many products. Biotech corn is strong against pests. This means less crop loss and more food. Farmers also use herbicide-resistant corn. This makes weed control easier and protects the crop.
- Insect Resistance: Protects from corn borers and rootworms.
- Herbicide Tolerance: Helps in managing weeds better.
- Drought Tolerance: Some biotech corn can survive in dry conditions.
Cotton
Cotton is essential for textiles. Biotech cotton has transformed this industry. It resists pests like the bollworm. This reduces the need for chemicals. Farmers produce more cotton with less effort. This biotech crop also helps the environment by reducing pesticide use.
- Pest Resistance: Protects against major cotton pests.
- Higher Yield: More cotton per acre.
- Environmental Benefits: Less pesticide use helps nature.
Beyond Conventional Produce
Biotech crops go beyond soybeans, corn, and cotton. Other examples include biotech potatoes and apples. These crops offer unique benefits. For instance, biotech potatoes resist bruising. Biotech apples do not brown quickly. Such innovations make food better and farming more sustainable.
| Crop | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Potatoes | Resist bruising and blight. |
| Apples | Do not brown quickly. |
Economic Impact Of Biotech Advances
Biotechnology in agriculture has transformed farming practices. It has brought significant economic benefits. These advances have reshaped the agricultural landscape. They have increased productivity and profitability for farmers. This section explores the economic impact of biotech advances. We will focus on yield improvements and global trade dynamics.
Yield Improvements
Biotech crops have led to higher yields. This means more food is grown on the same land.
- Increased Crop Resistance: Biotech crops resist pests and diseases better.
- Enhanced Growth Rates: These crops grow faster and stronger.
- Drought Tolerance: Some biotech crops need less water to thrive.
Higher yields mean more income for farmers. They can sell more produce and earn more money. This boosts the local economy. Farmers can invest in better equipment and technology. This cycle leads to continuous improvement and growth.
Global Trade Dynamics
Biotech advances have changed global trade. Countries can now produce more food. This affects how they trade with each other.
- Export Opportunities: Countries with biotech crops can export more.
- Import Reduction: They need to import less food.
- Market Stability: More food production leads to stable prices.
Trade dynamics affect global economies. Countries with biotech advances become more competitive. They can offer lower prices for higher quality produce. This strengthens their position in the global market.
| Economic Impact | Effect |
|---|---|
| Increased Yields | More income for farmers |
| Export Opportunities | Stronger global trade position |
| Market Stability | Stable prices and reduced import needs |
Biotechnology in agriculture is a game-changer. It improves yields and changes global trade dynamics. These economic impacts benefit farmers and nations alike.
Sustainable Practices Through Biotechnology
Biotechnology in agriculture enables sustainable practices. It helps to create a balance between crop production and environmental protection. Through biotechnology, farmers can reduce the need for harmful chemicals and conserve biodiversity. These practices lead to healthier ecosystems and more efficient farming.
Reducing Chemical Use
Biotechnology allows the development of pest-resistant crops. These crops reduce the need for chemical pesticides. Farmers can grow healthier plants with fewer chemicals.
Another innovation is herbicide-tolerant crops. These plants survive specific herbicides that target weeds. This reduces the overall chemical use on farms.
Biotechnology also improves disease resistance in crops. Plants become less prone to infections. This reduces the need for chemical treatments.
| Biotechnology Innovation | Impact on Chemical Use |
|---|---|
| Pest-resistant Crops | Less Pesticides |
| Herbicide-tolerant Crops | Targeted Weed Control |
| Disease-resistant Plants | Fewer Chemical Treatments |
Conserving Biodiversity
Biotechnology helps to conserve biodiversity by creating more resilient crops. These crops adapt better to changing environments. They also require fewer resources, preserving natural habitats.
Using biotechnology, farmers can grow a diverse range of crops. This reduces the reliance on a single crop type. A varied crop system supports different species of plants and animals.
Biotechnology also promotes the growth of native plants. These plants maintain the natural balance of ecosystems. They support local wildlife and improve soil health.
- Resilient crops adapt to changing environments.
- Diverse crops support various species.
- Native plants maintain ecosystem balance.

Credit: www.linkedin.com
Ethical Considerations And Public Perception
Biotechnology in agriculture brings many benefits. It also raises ethical questions and concerns. Public perception plays a huge role in its acceptance. This section dives into the ethical concerns and how the public views biotechnology.
Gmo Labeling Debate
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) are a big part of biotech in farming. The debate on GMO labeling is intense. Should foods with GMOs have special labels? Some argue that consumers have the right to know. Others believe labeling might cause unnecessary fear.
| Argument For Labeling | Argument Against Labeling |
|---|---|
| Informed consumer choice | Could create unfounded fear |
| Transparency and trust | Labeling costs |
| Health concerns | Scientific consensus on safety |
Those for labeling believe it promotes transparency and trust. They also highlight potential health concerns. Those against argue it may create fear without reason. Labeling also adds costs to producers.
Consumer Acceptance
Consumer acceptance of biotech in agriculture varies. Some embrace it for sustainability and efficiency. Others are wary of the unknown effects.
- Supporters value improved crop yields.
- Opponents worry about long-term health impacts.
- Environmental concerns also play a role.
Surveys show mixed feelings. Some consumers trust biotech foods. Others prefer organic and non-GMO options.
Building trust is key. Clear communication and education can help. Addressing ethical considerations openly can improve public perception.
Regulatory Landscape Governing Biotech Agriculture
Biotechnology in agriculture is transforming how we grow food. Yet, it brings new challenges. Understanding the regulatory landscape governing biotech agriculture is crucial. Different regions have different rules. These regulations ensure safety and efficacy. They also protect the environment and public health.
International Standards
International standards play a big role in biotech agriculture. Organizations like the Codex Alimentarius set global food safety standards. The Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety regulates the movement of living modified organisms. These standards help maintain safety across borders.
Here is a table summarizing key international standards:
| Organization | Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Codex Alimentarius | Food Safety | Ensure safety of food products |
| Cartagena Protocol | Biosafety | Regulate living modified organisms |
National Policies
Each country has its own national policies for biotech agriculture. The United States follows the Coordinated Framework for Biotechnology. This framework involves multiple agencies like the FDA, EPA, and USDA. They work together to regulate biotech products.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) plays a key role. EFSA assesses the safety of biotech products. They ensure these products are safe for humans, animals, and the environment.
Here is a list of some national policies:
- United States: Coordinated Framework for Biotechnology
- European Union: EFSA regulations
- Japan: Food Sanitation Act
- Australia: Gene Technology Act
These regulations ensure that biotech products are safe and effective. They protect public health and the environment. Understanding these regulations is important for anyone in the biotech field.

Credit: facts.net
Future Frontiers In Agricultural Biotechnology
Agricultural biotechnology is evolving rapidly. New advancements are reshaping farming. The future holds exciting possibilities. These innovations promise better yields and healthier crops.
Crispr And Gene Editing
CRISPR technology is a game-changer. It allows precise changes in DNA. Scientists can now edit genes in plants. This can make crops more resistant to pests.
Gene editing can also improve crop nutrition. For example, scientists can enhance vitamin content. This can help fight malnutrition. Farmers can grow healthier crops with better yields.
Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology combines biology and engineering. It creates new biological parts and systems. In agriculture, it can design crops with new traits. These traits can improve growth and resilience.
For example, synthetic biology can create drought-resistant crops. This is crucial in areas with water shortages. Farmers can maintain productivity even in tough conditions.
| Biotechnology Area | Benefits |
|---|---|
| CRISPR and Gene Editing | Pest resistance, improved nutrition |
| Synthetic Biology | Drought resistance, enhanced growth |
- Future of farming is bright.
- Technology drives agricultural success.
- Innovations lead to sustainable farming.
- Adopt new biotechnologies.
- Enhance crop resilience.
- Boost food security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Biotechnology Used For In Agriculture?
Biotechnology in agriculture enhances crop yields, improves resistance to pests and diseases, and boosts nutritional value. It also enables faster breeding processes and better adaptation to environmental stresses.
Which Is An Example Of Agricultural Biotechnology?
An example of agricultural biotechnology is genetically modified crops. These crops resist pests, diseases, and environmental conditions, increasing yield and efficiency.
What Is The Agricultural Biotechnology Process?
Agricultural biotechnology involves modifying plants, animals, and microorganisms. Scientists use techniques like genetic engineering to enhance crop yields, pest resistance, and nutritional value.
What Are The 4 Types Of Biotechnology?
The four types of biotechnology are red, green, white, and blue. Red focuses on medical applications. Green targets agricultural processes. White deals with industrial processes. Blue pertains to marine and aquatic environments.
Conclusion
Biotechnology in agriculture offers immense potential for sustainable farming. It enhances crop yields, reduces pests, and improves food security. Farmers benefit from advanced techniques and resilient crops. Embracing biotechnology can lead to a greener, more productive future. Stay informed and support innovations in agricultural biotechnology for a healthier planet.
