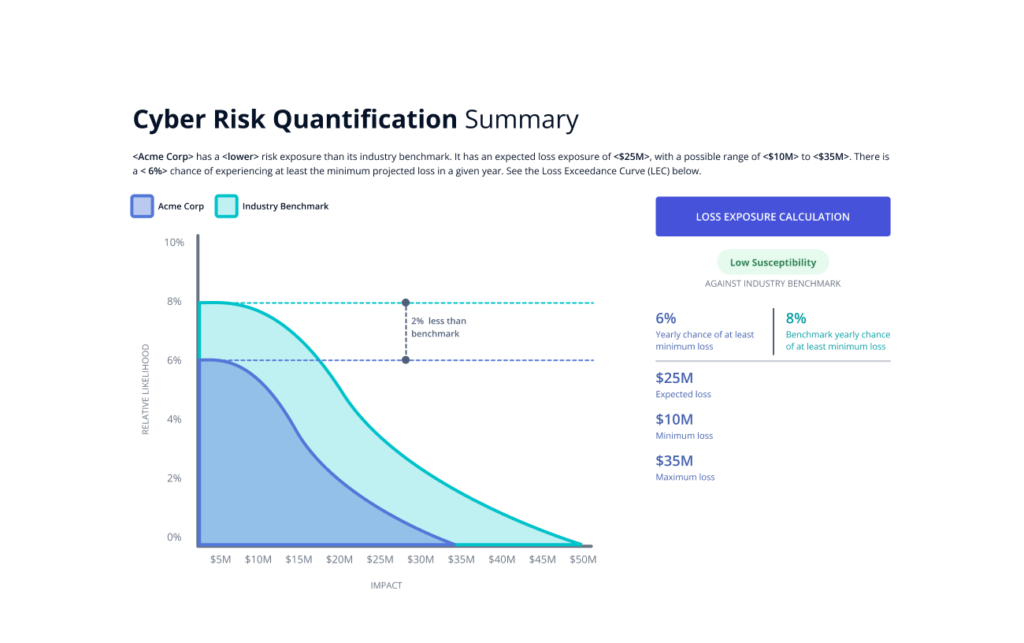
Cyber Risk Quantification measures the financial impact of cyber threats. It helps organizations understand and manage their cyber risks.
Cyber Risk Quantification is essential in today’s digital landscape. Businesses face increasing cyber threats that can cause significant financial losses. Quantifying these risks allows companies to allocate resources effectively and implement robust cybersecurity measures. Accurate risk quantification helps in making informed decisions, enhancing security posture, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
By understanding potential financial impacts, organizations can prioritize their cybersecurity investments. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of cyber incidents and mitigates their effects. Cyber Risk Quantification is a critical component of modern risk management strategies. It empowers businesses to safeguard their assets, reputation, and overall operational integrity.
Cyber Risk Quantification Explained
Cyber Risk Quantification is crucial in today’s digital age. It helps organizations understand and manage cyber threats. This process converts complex cyber risks into understandable financial terms. It allows businesses to make informed decisions and prioritize security investments.
The Need For Quantifying Cyber Risks
Every business faces cyber threats. These threats can cause significant financial losses and damage reputations. Quantifying cyber risks helps identify potential losses and prepare for them. It ensures that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently.
- Helps in understanding potential financial impact.
- Assists in prioritizing security measures.
- Enables better decision-making.
- Protects the company’s reputation and assets.
Businesses need to understand the financial impact of cyber risks. Quantifying these risks provides a clear picture. It helps in making strategic decisions.
Key Principles Of Cyber Risk Quantification
Several key principles guide the process of Cyber Risk Quantification. Understanding these principles is essential.
- Identify Assets: Identify all critical assets that need protection.
- Assess Vulnerabilities: Assess the vulnerabilities in each asset.
- Evaluate Threats: Evaluate potential threats that could exploit these vulnerabilities.
- Estimate Impact: Estimate the financial impact of these threats.
- Prioritize Risks: Prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood.
These principles ensure a structured approach to risk quantification. They provide a clear roadmap for identifying and managing cyber risks.
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Identify Assets | Recognize all critical assets that need protection. |
| Assess Vulnerabilities | Determine the weaknesses in each asset. |
| Evaluate Threats | Analyze potential threats that could exploit vulnerabilities. |
| Estimate Impact | Calculate the financial consequences of these threats. |
| Prioritize Risks | Rank risks based on their impact and likelihood. |
Cyber Risk Quantification is a vital process. It converts complex cyber risks into understandable financial terms. Understanding its principles is key to effective risk management.
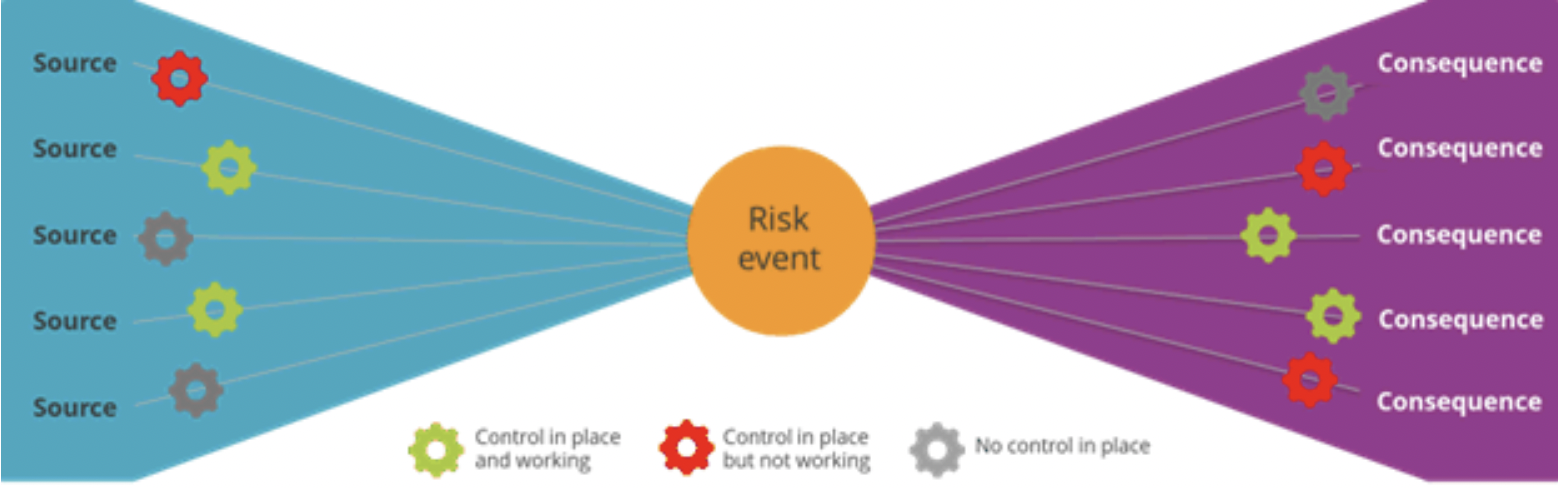
Credit: securityscorecard.com
Identifying Cyber Assets
Identifying cyber assets is crucial in understanding and mitigating cyber risks. Knowing what digital assets you have helps in crafting effective cybersecurity strategies. Let’s dive deeper into the steps of identifying cyber assets.
Inventory Of Digital Assets
Creating an inventory of digital assets is the first step. This inventory should include:
- Hardware: Servers, computers, mobile devices
- Software: Operating systems, applications, databases
- Data: Customer information, financial records, intellectual property
Use asset management tools to automate this process. These tools can scan networks and list all connected devices. Keeping this inventory up-to-date is essential.
Critical Asset Prioritization
Not all assets have the same level of importance. Prioritizing critical assets helps in focusing security efforts. Consider the following factors:
- Value of the Asset: How important is the asset to your business?
- Impact of Loss: What would be the impact if the asset is compromised?
- Exposure to Threats: How likely is the asset to be targeted?
By prioritizing, you can allocate resources efficiently. Focus on protecting the most critical assets first.
Here’s a table to help you visualize this process:
| Asset | Value | Impact of Loss | Exposure to Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Data | High | Severe | High |
| Financial Records | High | Severe | Medium |
| Application Servers | Medium | Moderate | High |
This table helps in understanding which assets need more protection. It also helps in making informed security decisions.
Threat Landscape Assessment
Understanding the threat landscape is crucial for effective cyber risk quantification. This involves identifying current cyber threats and analyzing historical data. Both steps help organizations prepare better defenses. Let’s dive into the key aspects of a threat landscape assessment.
Current Cyber Threats
Current cyber threats are constantly evolving. Hackers use advanced techniques to breach systems. Organizations must stay updated on these threats.
- Phishing Attacks: Hackers trick users into giving personal information.
- Ransomware: Malicious software locks data until a ransom is paid.
- Malware: Software designed to harm or exploit systems.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors who misuse access to data.
Historical Data Analysis
Historical data analysis helps in understanding past cyber threats. This analysis provides insights into patterns and trends. Organizations can predict future threats by studying historical data.
| Year | Major Cyber Threat | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Ransomware | Global disruptions, costly recoveries |
| 2021 | Phishing | Data breaches, financial losses |
| 2022 | Supply Chain Attacks | Widespread system compromises |
Analyzing historical data helps in understanding which threats have been most damaging. This aids in prioritizing security measures.
Vulnerability Evaluation
Vulnerability evaluation is a crucial part of cyber risk quantification. It involves identifying and assessing potential weaknesses in a system. This helps in understanding the level of risk and planning appropriate mitigation strategies.
Technical Weaknesses
Technical weaknesses are flaws in the software or hardware. These can be exploited by attackers. Identifying these weaknesses is essential for protecting your system.
- Software Bugs: Coding errors that can be exploited.
- Unpatched Systems: Systems that lack the latest security updates.
- Configuration Errors: Mistakes in setting up software or hardware.
Conduct regular scans to find and fix these issues. Use automated tools and manual reviews to ensure thoroughness.
Human Factor Considerations
The human factor is a significant aspect of vulnerability evaluation. People can make mistakes that expose systems to risk. Evaluating these risks involves understanding how employees interact with systems and data.
- Phishing Attacks: Employees might click on malicious links.
- Weak Passwords: Easy-to-guess passwords can be a major risk.
- Insufficient Training: Lack of knowledge about security practices.
Training programs can help mitigate these risks. Educate employees about secure practices and the importance of vigilance.
| Weakness Type | Description | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Software Bugs | Errors in code that can be exploited. | Regular code reviews and updates. |
| Unpatched Systems | Systems missing security updates. | Automated patch management. |
| Phishing Attacks | Malicious emails targeting employees. | Employee training and email filters. |
Impact Analysis Techniques
Understanding the impact of cyber threats is crucial. It helps organizations safeguard their assets. Impact Analysis Techniques provide a structured way to evaluate these risks. These techniques cover both financial and reputational impacts.
Financial Impact Estimation
Estimating financial impacts involves calculating potential losses. These losses can include direct costs such as fines and indirect costs like loss of business. Companies should consider various factors to estimate these costs accurately.
- Direct Costs: These include fines, legal fees, and compensation payouts.
- Indirect Costs: These involve loss of business, increased insurance premiums, and operational disruptions.
Using historical data is one effective method. It helps in predicting future costs based on past incidents. Another method is scenario analysis. It involves creating hypothetical scenarios to understand potential losses.
| Cost Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Direct Cost | Legal fees for breach |
| Indirect Cost | Loss of business |
Reputation Damage Assessment
Reputation damage can be more costly than financial losses. It affects customer trust and brand value. Assessing this damage is essential for maintaining long-term success.
- Customer Surveys: Ask customers about their trust and perception.
- Social Media Monitoring: Track mentions and sentiments on social platforms.
- Media Analysis: Evaluate coverage in news and blogs.
Customer surveys provide direct feedback. They help gauge customer trust levels after a cyber incident. Social media monitoring offers real-time insights. It tracks how people talk about your brand online. Media analysis helps understand the broader public perception.
Combining these methods gives a clear picture of reputation damage. It helps in crafting effective response strategies.
Probability Determination
Determining the probability of cyber risks is crucial for any organization. This process helps in understanding the potential threats that could impact the business. By assessing the likelihood of these threats, companies can better prepare and allocate resources to mitigate risks.
Assessing Likelihood Of Threats
Assessing the likelihood of threats involves evaluating various factors that can lead to a cyber attack. These factors include the type of threat, frequency of past incidents, and vulnerability of systems.
Historical data is often analyzed to identify patterns. If a particular threat has occurred frequently in the past, it is more likely to happen again. Expert opinions and industry reports also play a significant role in this assessment.
Another important factor is the vulnerability of the organization’s systems. Systems with weak security measures are more likely to be targeted. Regular security audits help identify these weaknesses and improve defenses.
Statistical Models In Risk Assessment
Statistical models are essential tools in cyber risk quantification. They help in estimating the probability of different threats. These models use data analysis and probability theory to provide accurate estimates.
One common model is the Poisson distribution. This model helps in predicting the likelihood of rare events, such as cyber attacks. Another useful model is the Bayesian network. This model considers multiple factors and their interdependencies to assess risk.
Here is a simple example of how statistical models can be used:
| Threat Type | Probability |
|---|---|
| Phishing Attack | 0.30 |
| Malware Infection | 0.20 |
| Data Breach | 0.15 |
In the table, the probability values are derived from statistical models. These values help organizations prioritize their security measures.
Using statistical models allows for more accurate and data-driven decisions. It ensures that the organization is well-prepared for potential threats.
Integrating Cyber Risk Into Business Strategy
Cyber risks are a significant threat to modern businesses. Integrating cyber risk into your business strategy is essential. This ensures the security measures align with your business goals. It also helps communicate the risks effectively to stakeholders.
Aligning Security With Business Objectives
Aligning security with business objectives is crucial. It creates a cohesive strategy that supports the company’s mission. Here are some steps to achieve this:
- Identify Key Business Goals: Understand the primary goals of your business. This helps in prioritizing security efforts.
- Map Cyber Risks: Identify potential cyber threats that could impact these goals. Use risk assessments to find vulnerabilities.
- Develop a Response Plan: Create a plan to address identified risks. Ensure the plan supports the business objectives.
- Allocate Resources: Direct resources to high-priority areas. This ensures the most critical threats are managed first.
Communicating Risk To Stakeholders
Effective communication is key to managing cyber risks. Stakeholders need to understand the risks and their potential impact. Here are some tips for communicating risk:
- Use Clear Language: Avoid technical jargon. Use simple terms that everyone can understand.
- Provide Context: Explain how the risks relate to the business goals. This helps stakeholders see the bigger picture.
- Show Data: Use data to illustrate the risks. Charts and graphs can be very effective.
- Highlight Benefits: Explain how addressing the risks can benefit the business. Focus on long-term gains.
Here’s a simple table to summarize the key points:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| Identify Key Business Goals | Understand the primary objectives of the business. |
| Map Cyber Risks | Identify threats that could impact business goals. |
| Develop a Response Plan | Create a plan to address the identified risks. |
| Allocate Resources | Direct resources to manage critical threats first. |
| Use Clear Language | Avoid technical jargon when communicating risks. |
| Provide Context | Explain how risks relate to business goals. |
| Show Data | Use data to illustrate the risks. |
| Highlight Benefits | Explain the benefits of addressing the risks. |
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Cyber risk quantification helps organizations understand their exposure to cyber threats. Risk mitigation strategies are essential to minimize these risks. This section explores effective strategies to safeguard your digital assets.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are the first line of defense against cyber threats. Implementing these measures can significantly reduce the risk of cyber attacks.
- Regular Software Updates: Ensure all software is up-to-date to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce the use of complex passwords and regular password changes.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security with MFA.
- Employee Training: Educate employees on recognizing phishing scams and other cyber threats.
- Firewall and Antivirus Software: Use robust firewall and antivirus software to detect and prevent threats.
Incident Response Planning
Even with preventive measures, incidents can occur. Incident response planning ensures that your organization is prepared to respond effectively.
- Create an Incident Response Team: Form a dedicated team to handle cyber incidents.
- Develop a Response Plan: Outline the steps to take during a cyber incident.
- Regular Drills: Conduct regular drills to ensure the team is prepared.
- Communication Strategy: Establish a clear communication plan for stakeholders.
- Post-Incident Analysis: Analyze incidents to improve future response strategies.
Effective risk mitigation strategies are crucial for protecting your organization. By implementing preventive measures and having an incident response plan, you can minimize the impact of cyber threats.
Continuous Monitoring & Improvement
In the dynamic world of cybersecurity, continuous monitoring and improvement are essential. Cyber threats evolve rapidly, demanding constant vigilance. Organizations must stay ahead by continuously monitoring their systems. This ongoing process helps identify and mitigate risks promptly.
Real-time Threat Intelligence
Real-time threat intelligence is critical in cyber risk quantification. It involves gathering and analyzing data as threats emerge. This approach provides immediate insights into potential risks.
Organizations use various tools and technologies for real-time threat intelligence:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Identify and alert on suspicious activities.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Aggregate and analyze security data.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIP): Correlate data from multiple sources.
These tools help organizations stay informed and proactive. They enable quick responses to emerging threats, minimizing potential damage.
Adapting To Evolving Risks
Cyber risks constantly change. Adapting to evolving risks is vital for effective cyber risk quantification. Organizations must regularly update their security measures.
Strategies for adapting to evolving risks include:
- Conducting frequent risk assessments.
- Implementing regular security training for employees.
- Updating software and systems to patch vulnerabilities.
- Using automated tools for continuous monitoring.
By staying adaptable, organizations can address new threats quickly. This proactive approach ensures robust security and minimizes risks.
Continuous monitoring and improvement are cornerstones of effective cyber risk quantification. Real-time threat intelligence and adapting to evolving risks are key components. By focusing on these areas, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect their assets.

Credit: elasticito.com
Regulatory Compliance And Reporting
In the realm of Cyber Risk Quantification, Regulatory Compliance and Reporting play a pivotal role. Businesses must navigate complex legal landscapes. Transparent reporting practices are essential to maintain trust and avoid penalties.
Navigating Legal Requirements
Understanding the legal requirements for cyber risk is crucial. Different regions have varied laws. Companies must stay updated with these laws.
Here is a table summarizing key regulations:
| Region | Regulation | Key Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| EU | GDPR | Data protection and breach notification |
| USA | CCPA | Consumer data privacy |
| APAC | APPI | Personal information protection |
Each regulation demands specific actions. Compliance ensures companies avoid hefty fines. It also protects their reputation.
Transparent Reporting Practices
Transparent reporting is vital for regulatory compliance. It builds trust with stakeholders. Companies must report breaches and risks clearly.
Follow these best practices for transparent reporting:
- Regular audits to identify risks.
- Clear documentation of all findings.
- Immediate reporting of breaches.
- Training employees on compliance.
Transparent practices also involve stakeholders. This includes shareholders, customers, and regulators. They should be informed about risks and actions taken.
Adopting these practices ensures compliance. It also builds a strong cybersecurity culture within the organization.
Cyber Insurance Considerations
Cyber insurance is essential for businesses. It helps manage risks associated with cyber threats. Understanding your coverage options and calculating your insurance needs is crucial.
Coverage Options
Cyber insurance offers different coverage options. Below are some common options:
- First-party coverage: Protects your business directly affected by a cyber event.
- Third-party coverage: Covers claims made by clients or partners affected by your cyber incident.
- Data breach response: Covers costs related to data breach notifications and credit monitoring.
- Business interruption: Covers loss of income due to cyber incidents.
- Cyber extortion: Covers ransom payments and investigation costs.
Calculating Insurance Needs
Calculating your cyber insurance needs is essential. Consider these steps:
- Assess your risk exposure: Identify potential cyber threats and vulnerabilities in your systems.
- Evaluate potential impact: Analyze the financial impact of a cyber event on your business.
- Determine coverage limits: Decide how much coverage you need to protect against potential losses.
- Review policy exclusions: Understand what is not covered by your policy to avoid surprises.
- Consult with experts: Seek advice from insurance professionals to tailor coverage to your needs.
| Coverage Option | Description |
|---|---|
| First-party coverage | Protects your business directly affected by a cyber event. |
| Third-party coverage | Covers claims made by clients or partners affected by your cyber incident. |
| Data breach response | Covers costs related to data breach notifications and credit monitoring. |
| Business interruption | Covers loss of income due to cyber incidents. |
| Cyber extortion | Covers ransom payments and investigation costs. |
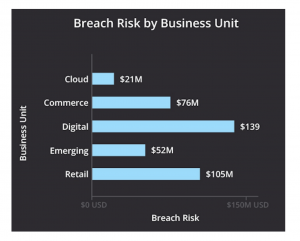
Credit: www.balbix.com
Case Studies: Successful Quantification
Cyber Risk Quantification (CRQ) offers a precise way to assess cyber threats. Real-world case studies highlight its effectiveness. These examples show how different industries use CRQ to protect their data and operations.
Industry-specific Examples
Various industries face unique cyber risks. Here are some examples:
| Industry | Case Study | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Hospital A used CRQ to identify vulnerabilities. | Reduced data breaches by 50%. |
| Finance | Bank B implemented CRQ to enhance security protocols. | Decreased cyberattack costs by $1 million. |
| Retail | Retailer C applied CRQ to protect customer data. | Improved customer trust by 30%. |
Lessons Learned From Security Breaches
Security breaches teach valuable lessons. Successful CRQ implementation prevents future attacks. Here are key takeaways:
- Identify Weak Points: CRQ helps pinpoint system vulnerabilities.
- Cost Reduction: Quantifying risks reduces financial losses.
- Enhanced Trust: Securing data boosts customer confidence.
- Proactive Measures: CRQ enables proactive cybersecurity strategies.
Cyber Risk Quantification is essential for modern businesses. Understanding industry-specific examples and lessons from breaches can guide better cybersecurity practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Is Cybersecurity Risk Measured?
Cybersecurity risk is measured by assessing potential threats, vulnerabilities, and the impact on assets. This includes evaluating the likelihood of attacks and potential damage.
What Is Quantitative Cybersecurity Risk?
Quantitative cybersecurity risk measures potential financial losses from cyber threats using data and mathematical models. It helps prioritize security efforts effectively.
What Is The Risk Quantification Method?
Risk quantification method identifies, measures, and evaluates risks using statistical models and data analysis techniques. It helps prioritize risks.
What Is Cyber Risk Quantification Deloitte?
Cyber risk quantification by Deloitte measures financial impact of cyber threats. It helps organizations prioritize and manage risks effectively.
Conclusion
Quantifying cyber risk is essential for effective cybersecurity strategies. It helps businesses understand potential threats and allocate resources wisely. By implementing robust cyber risk quantification methods, companies can better protect their assets. Stay ahead of cyber threats by embracing comprehensive risk assessment tools.
This proactive approach ensures long-term security and resilience in the digital age.