Distributed Cloud refers to the deployment of cloud services across multiple locations, including on-premises and edge environments. It enhances performance and compliance by placing services closer to users.
Distributed Cloud offers a revolutionary approach to cloud computing. It decentralizes cloud resources, making them accessible from various locations. This model improves latency, regulatory compliance, and disaster recovery. Businesses can leverage Distributed Cloud to optimize performance by reducing data travel distance.
It also allows for more robust data sovereignty, adhering to local data protection laws. As the demand for low-latency applications grows, Distributed Cloud becomes essential. Companies can benefit from its agility, scalability, and resilience. Embracing Distributed Cloud can significantly enhance operational efficiency and user experience.
Introduction To Distributed Cloud
The world of cloud computing is evolving rapidly. Distributed Cloud represents the latest innovation in this field. It offers unprecedented flexibility and scalability for businesses. This section explores the fundamental aspects of Distributed Cloud.
Definition And Concept
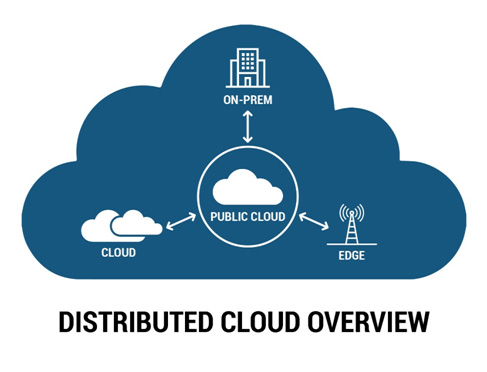
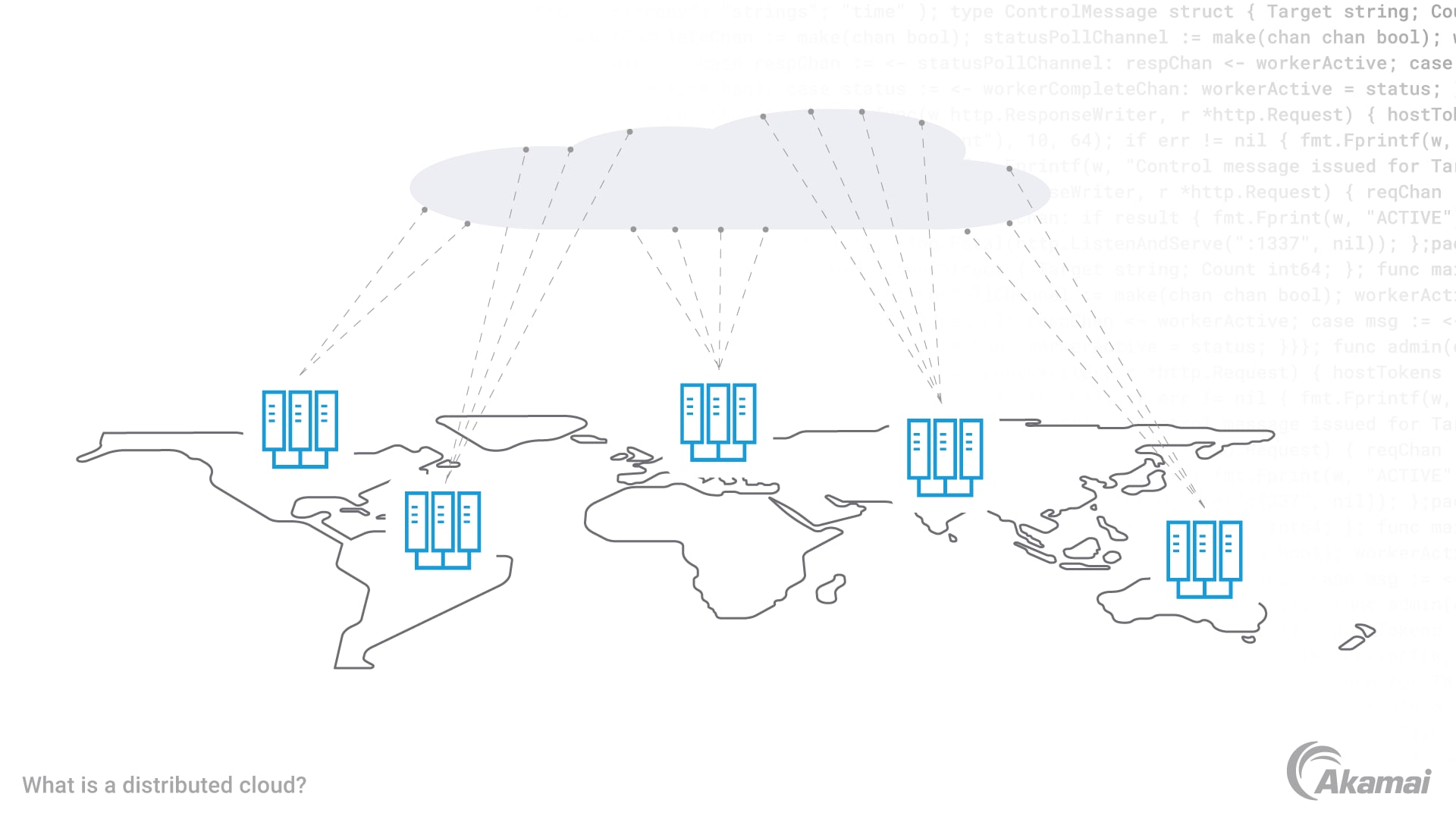
Distributed Cloud refers to the distribution of public cloud services. These services are spread across different physical locations. The aim is to maintain the same control and management as a centralized cloud. This unique architecture ensures data and applications are closer to the end users. It enhances performance and reduces latency.
In a Distributed Cloud model, the cloud provider manages and operates the distributed infrastructure. Customers benefit from a unified cloud experience. This approach combines the advantages of centralized cloud and edge computing.
Importance In Modern It
Distributed Cloud plays a crucial role in modern IT. It caters to the growing demand for low-latency services. Businesses rely on real-time data processing and fast response times.
Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Performance: Data is closer to users, reducing latency.
- Improved Reliability: Distributed infrastructure ensures redundancy.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources based on demand.
- Compliance: Meet regional data regulations more efficiently.
These benefits make Distributed Cloud an essential component for IT strategies. Businesses can deliver seamless and efficient services to their customers.
Core Components
The core components of a distributed cloud system ensure seamless operations. They form the backbone of any distributed cloud architecture. Understanding these core components is essential for leveraging the full potential of distributed cloud technology.
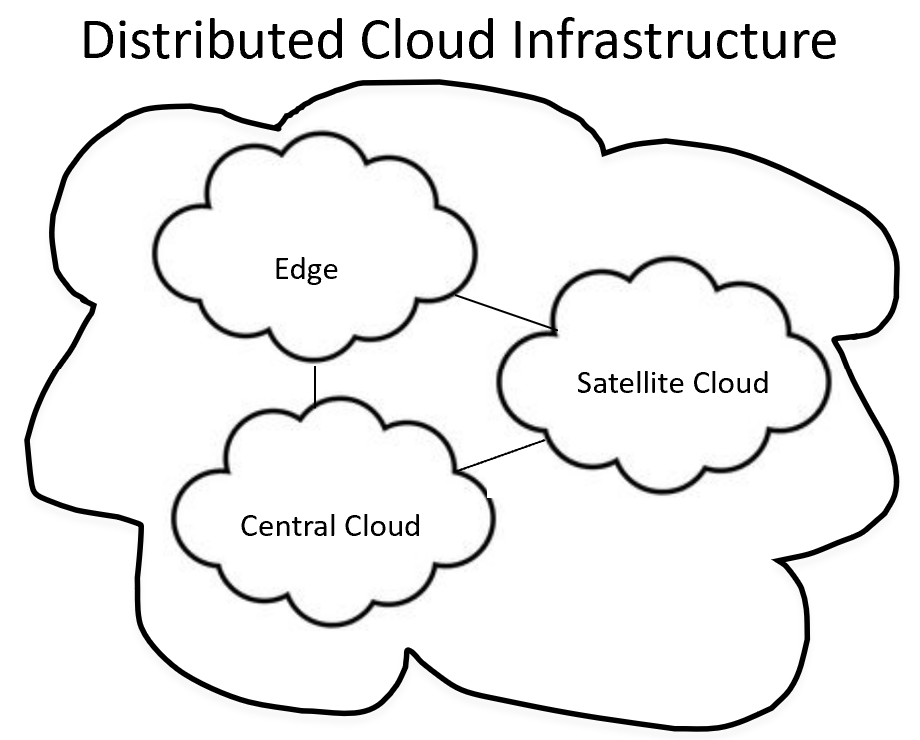
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to data sources. This reduces latency and enhances speed. Devices at the edge handle processing tasks, reducing the load on central servers. Edge computing supports real-time data processing. It is ideal for applications requiring quick responses.
- Reduces latency
- Enhances processing speed
- Supports real-time data processing
Edge computing often works with IoT devices. These devices generate massive data that require immediate processing. This proximity ensures faster decision-making and improves efficiency.
Central Cloud Services
Central cloud services act as the brain of distributed cloud systems. They offer centralized control and management. These services provide robust data storage and processing power. Central cloud services ensure data integrity and security.
- Centralized control and management
- Robust data storage
- Enhanced data integrity and security
The central cloud integrates with edge nodes, creating a cohesive system. It supports various applications, from AI to big data analytics. This integration ensures a balanced load and optimized performance.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Edge Computing | Reduces latency and enhances real-time processing. |
| Central Cloud Services | Offers centralized control, data storage, and processing. |
Benefits
Distributed Cloud offers numerous benefits for businesses. This section explores key advantages, focusing on scalability and enhanced performance.
Scalability
Distributed Cloud provides unmatched scalability. Businesses can easily adjust their resources. This means handling traffic spikes without issues.
With a distributed cloud, you can scale horizontally and vertically. Horizontal scaling adds more machines to your cloud. Vertical scaling increases the power of existing machines.
Scaling is automatic and seamless. This ensures that applications run smoothly at all times.
| Type | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Horizontal Scaling | Add more machines |
| Vertical Scaling | Increase machine power |
Enhanced Performance
Distributed Cloud offers enhanced performance by reducing latency. Data is processed closer to the user. This means faster response times.
Applications can be distributed geographically. This ensures that data is closer to users. The result is quicker access and improved performance.
- Faster response times
- Reduced latency
- Improved user experience
Enhanced performance also leads to better resource utilization. Each part of the cloud operates efficiently. This reduces waste and maximizes output.
Credit: www.turningcloud.com
Challenges
The distributed cloud presents a range of challenges that businesses must navigate. These challenges can impact performance, security, and manageability. Let’s delve into some of the key challenges faced in distributed cloud environments.
Security Concerns
One of the primary challenges in a distributed cloud is ensuring data security. Data is spread across multiple locations, making it more vulnerable. This can lead to various security risks, such as:
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Compliance issues: Difficulty meeting regulatory requirements.
- Data integrity: Ensuring data remains accurate and unaltered.
Implementing robust security measures is essential. Encryption, access controls, and regular audits can help. Organizations must also stay updated with the latest security threats and solutions.
Complex Management
Managing a distributed cloud environment can be highly complex. Each cloud instance might have its own set of tools and protocols. This can lead to several management challenges, such as:
- Resource allocation: Efficiently distributing resources across multiple locations.
- Performance monitoring: Keeping track of performance metrics in real-time.
- Incident response: Quickly addressing and resolving any issues that arise.
To tackle these challenges, organizations often use centralized management tools. These tools help streamline processes and provide a unified view of the entire cloud environment. Automation can also play a significant role in reducing management complexity.
Below is a table summarizing the key challenges and potential solutions:
| Challenge | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|
| Security Concerns | Encryption, access controls, regular audits |
| Complex Management | Centralized management tools, automation |
Use Cases
The distributed cloud is a game-changer for many industries. It offers unique solutions for various use cases. Below, we explore some key applications.
Iot Applications
Internet of Things (IoT) devices generate vast amounts of data. The distributed cloud can handle this data efficiently. It processes data close to the source. This reduces latency and improves performance.
IoT applications include:
- Smart homes
- Wearable devices
- Connected cars
- Industrial automation
In smart homes, devices like thermostats and lights connect to the cloud. They respond faster due to local processing. Wearable devices monitor health data in real-time. This helps in quick medical responses.
Data Analytics
Data analytics is crucial for many businesses. The distributed cloud makes data analytics more efficient. It processes data where it is generated. This is known as edge computing.
Key benefits include:
- Faster insights
- Reduced data transfer costs
- Improved data security
A table can illustrate these benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Faster insights | Data is processed locally, reducing delay. |
| Reduced costs | Less data needs to be sent to central servers. |
| Improved security | Data stays close to its source, reducing risk. |
Businesses can use distributed cloud for real-time analytics. This helps in making quicker decisions. It is especially useful in sectors like finance and retail.
Credit: www.techopedia.com
Implementation Strategies
Implementing a distributed cloud requires careful planning and execution. Here, we discuss effective strategies for seamless integration. These strategies ensure optimal performance and scalability.
Hybrid Models
Hybrid models combine public and private clouds. This method leverages the strengths of both. Public clouds offer scalability and cost-efficiency. Private clouds ensure security and control.
A balanced hybrid approach optimizes workloads. Sensitive data stays in private clouds. Compute-intensive tasks move to public clouds. This strategy enhances flexibility and resource management.
- Scalable resources
- Cost-efficient solutions
- Enhanced security
Migration Tips
Migrating to a distributed cloud involves several steps. Planning is crucial. Start with a comprehensive assessment. Identify workloads suitable for migration.
Prioritize applications based on complexity. Migrate simpler workloads first. This reduces initial risks. Use automation tools for smoother transitions. Minimize downtime with phased migrations.
- Assess current infrastructure
- Identify suitable workloads
- Prioritize simple applications
- Use automation tools
- Implement phased migrations
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Assessment | Evaluate existing infrastructure |
| Identification | Find workloads for migration |
| Prioritization | Migrate simpler applications first |
| Automation | Use tools for smooth transitions |
| Phased Migration | Reduce downtime with phased approach |
Future Trends
The future of distributed cloud is rapidly evolving. Several trends are shaping its landscape. These trends promise to revolutionize how businesses operate. Below, we explore some key future trends.
Ai Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing distributed cloud systems. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data quickly. This enhances decision-making and operational efficiency. AI can also predict system failures before they happen. This helps in maintaining uptime and reliability.
AI-driven analytics enable more personalized user experiences. This makes services more engaging and user-friendly. AI can optimize resource allocation in distributed cloud environments. This ensures that resources are used efficiently and cost-effectively.
5g And Beyond
5G technology brings faster data speeds and lower latency. This is crucial for distributed cloud systems. 5G allows for real-time data processing and analytics. This supports applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
Future advancements in 5G will further enhance distributed cloud capabilities. This includes better connectivity and more robust security features. Beyond 5G technologies will offer even greater bandwidth and faster speeds. This will open new possibilities for innovation and development.
Here’s a quick comparison of AI and 5G benefits:
| AI Integration | 5G and Beyond |
|---|---|
| Improves decision-making | Faster data speeds |
| Predicts system failures | Lower latency |
| Enhances user experiences | Real-time processing |
| Optimizes resource allocation | Better connectivity |
Both AI and 5G are essential for the future of distributed cloud. They offer unique benefits that will transform various industries.
Credit: www.akamai.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Example Of A Distributed Cloud?
An example of a distributed cloud is Google Cloud Platform. It uses multiple data centers worldwide for enhanced performance and reliability.
What Is The Difference Between Distributed Cloud And Cloud Computing?
Distributed cloud uses multiple interconnected clouds for data processing. Cloud computing relies on centralized data centers for services.
What Is A Distributed System In Cloud Computing?
A distributed system in cloud computing connects multiple computers to work together. They share resources and tasks, enhancing performance and reliability. These systems efficiently handle large-scale data processing and complex computations. Cloud platforms utilize distributed systems for scalability, fault tolerance, and flexible resource management.
What Is The Main Advantage Of Distributed Cloud?
The main advantage of distributed cloud is improved performance and reliability through localized data processing and reduced latency.
Conclusion
Embracing distributed cloud technology can transform your business operations. It offers flexibility, scalability, and enhanced security. Stay ahead by adopting this innovative approach. Harness the power of distributed cloud to optimize your IT infrastructure. Make the switch today and experience unparalleled performance and efficiency.