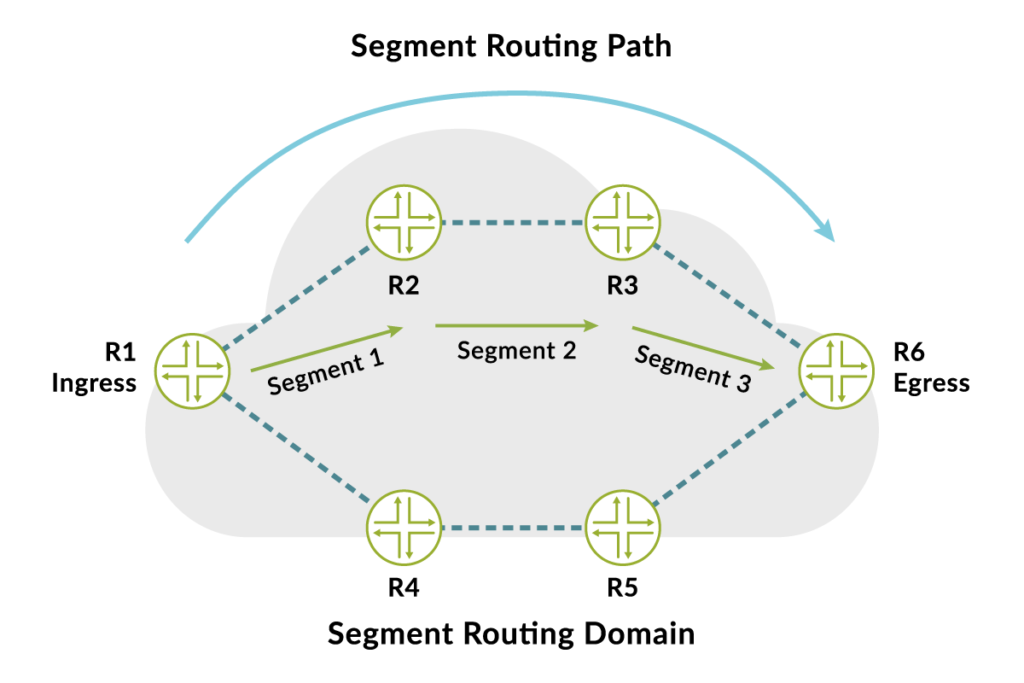
Segment Routing (SR) simplifies network traffic management by encoding paths into packet headers. It eliminates the need for traditional stateful protocols.
Segment Routing is a modern network architecture designed to enhance the efficiency of data packet routing. It uses a source-routing mechanism, where the source of the packet defines the entire path through the network. This approach reduces the complexity of network protocols and increases flexibility.
Segment Routing is highly scalable, making it ideal for large-scale networks. It improves traffic engineering, optimizes resource utilization, and enhances network reliability. By embedding routing information directly into packet headers, Segment Routing eliminates the need for intermediate routers to maintain complex state information. This results in a more streamlined and efficient network operation.
Introduction To Segment Routing
Segment Routing is changing network routing. It brings flexibility and efficiency. This technology is transforming how networks operate.
What Is Segment Routing?
Segment Routing (SR) is a modern routing method. It simplifies packet forwarding. It uses a list of instructions called segments. These segments guide packets through the network.
In traditional routing, each router decides the packet’s next hop. With Segment Routing, the packet’s path is pre-determined. This reduces complexity and improves performance.
Segment Routing supports different use cases:
- Traffic Engineering
- Network Slicing
- Service Chaining
Historical Context
Routing has evolved over time. Early networks used static routes. Routers had fixed paths for packets. This was simple but not flexible.
Later, dynamic routing protocols emerged. These protocols, like OSPF and BGP, adapted to network changes. They offered more flexibility but added complexity.
| Era | Routing Method | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Early Networks | Static Routing | Fixed paths, simple, inflexible |
| Dynamic Protocols | OSPF, BGP | Adaptive, complex, scalable |
Segment Routing is the next step. It combines simplicity and flexibility. It uses source routing principles. The source node defines the packet’s path. This reduces the need for complex protocols.
Segment Routing also supports IPv6. This is crucial for modern networks. It ensures compatibility and scalability.

Credit: www.networkurge.com
Key Components
Understanding the key components of Segment Routing is crucial. This knowledge helps in grasping the concept fully. Let’s explore the essential parts that make up Segment Routing.
Segments
In Segment Routing, a segment is a path or instruction. It tells packets where to go in the network. Segments act like directions in a map. They guide packets from one point to another.
Segments come in two types:
- Node Segments – Direct packets to a specific node.
- Adjacency Segments – Direct packets over a specific link.
These segments ensure efficient routing. They provide flexibility and control over the network path.
Segment Identifiers
Segment Identifiers (SIDs) are unique labels. They identify each segment in the network. SIDs play a vital role in Segment Routing.
There are different types of SIDs:
- Node SID – Identifies a specific network node.
- Adjacency SID – Identifies a specific link between nodes.
- Anycast SID – Identifies a group of nodes.
The SID is encoded in the packet header. It tells the network how to handle the packet. This makes routing simpler and more efficient.
How Segment Routing Works
Understanding how Segment Routing works is crucial in optimizing network performance. By directing traffic along specific paths, Segment Routing enhances efficiency and flexibility.
Packet Forwarding
Segment Routing leverages a predetermined path for packet forwarding. Each packet contains a list of segments to follow, simplifying network operations.
Path Computation
Segment Routing calculates the optimal path based on network conditions. This dynamic approach ensures efficient traffic flow.
Benefits Of Segment Routing
Segment Routing provides many advantages for modern networks. It simplifies network operations, enhances traffic engineering, and improves overall efficiency. Let’s explore these benefits in detail.
Simplified Network Operations
Segment Routing reduces the need for complex protocols. It allows for simpler configurations. Network administrators can manage paths with fewer resources. This leads to a more efficient network.
With Segment Routing, there is no need for state in the core network. This results in fewer points of failure. It also allows for faster troubleshooting and maintenance.
Automation is another key advantage. Segment Routing supports automated path computation. This reduces manual intervention and human error.
Enhanced Traffic Engineering
Segment Routing improves traffic management. It allows for precise control over data paths. Network operators can optimize routes based on various criteria.
Using Segment Identifiers (SIDs), operators can direct traffic efficiently. This leads to better bandwidth utilization. It also helps in avoiding congestion and ensuring smooth data flow.
Segment Routing also supports fast reroute. In case of a failure, traffic can be redirected quickly. This ensures high availability and reliability of the network.
Segment Routing Vs Traditional Routing
Segment Routing (SR) and Traditional Routing are two distinct methods for directing data traffic across networks. Both have their unique strengths and uses. Understanding their differences can help in choosing the right method for a specific need.
Efficiency Comparison
Segment Routing simplifies the process by encoding the path information within the packet headers. This reduces the need for complex signaling protocols.
Traditional Routing relies on dynamic protocols to determine the best path. This can introduce delays and complexities in high-traffic scenarios.
| Aspect | Segment Routing | Traditional Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Path Encoding | Encoded in packet headers | Determined dynamically |
| Protocol Complexity | Less complex | More complex |
| Latency | Lower | Higher |
Scalability Differences
Segment Routing offers superior scalability. It reduces the state information needed in network nodes.
- Minimal state information
- Scales well with network growth
Traditional Routing requires each node to maintain extensive state information. This limits its scalability.
- High state information
- Challenges with network expansion
In summary, Segment Routing provides a more efficient and scalable solution compared to Traditional Routing. Understanding these differences helps in making informed decisions for network management.
Use Cases
Segment Routing (SR) is a powerful technology that simplifies network operations. It is versatile and provides numerous advantages across different scenarios. Below, we explore two primary use cases: Data Centers and Service Providers.
Data Centers
Data Centers benefit significantly from Segment Routing. It enhances network efficiency and reduces operational complexity.
- Traffic Engineering: SR enables precise traffic steering, improving bandwidth utilization.
- Fast Reroute: It ensures quick recovery from failures, minimizing downtime.
- Scalability: SR supports seamless scaling without complex configurations.
These features are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and reliability in data centers.
Service Providers
Service Providers leverage Segment Routing to deliver better services and reduce costs. It offers flexibility and control over network traffic.
- Optimized Routing: SR allows dynamic path adjustments, enhancing service quality.
- Cost Reduction: It decreases reliance on traditional MPLS, lowering expenses.
- Service Differentiation: Providers can offer customized services, improving customer satisfaction.
These benefits make Segment Routing a valuable tool for modern Service Providers.
| Use Case | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Data Centers | Traffic Engineering, Fast Reroute, Scalability |
| Service Providers | Optimized Routing, Cost Reduction, Service Differentiation |
Challenges And Considerations
Segment Routing (SR) offers many benefits, but it also brings challenges. Understanding these challenges helps in better planning and deployment. This section dives into the key challenges and considerations of SR.
Implementation Hurdles
Implementing Segment Routing can be complex. Existing infrastructure might need upgrades. Ensure all network devices support SR.
- Hardware Compatibility: Check if your routers support SR.
- Software Updates: Update network software to enable SR features.
- Staff Training: Train your IT staff on SR protocols and management.
Implementing SR demands careful planning. Evaluate your network’s readiness before starting.
Security Concerns
Security is crucial in Segment Routing. SR can introduce new vulnerabilities.
- Path Manipulation: Attackers might alter the routing paths.
- Data Integrity: Ensure data packets are not tampered with.
- Authentication: Use strong authentication methods to secure SR paths.
Security measures must be robust. Regularly update security protocols and monitor the network.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Hardware Compatibility | Upgrade routers to support SR. |
| Software Updates | Regularly update network software. |
| Path Manipulation | Implement strict path validation. |
| Data Integrity | Use encryption to protect data. |
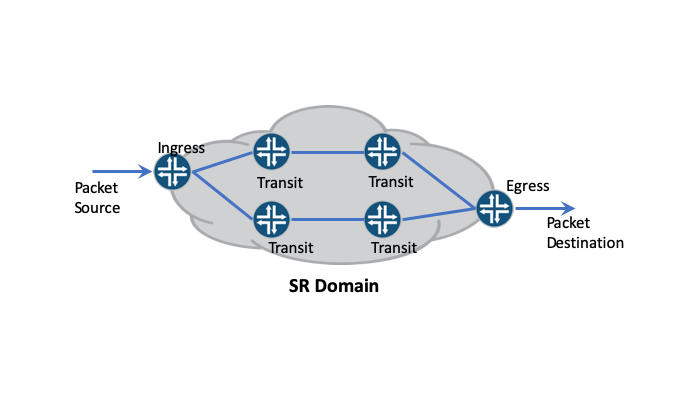
Credit: blogs.juniper.net
Future Of Segment Routing
The future of Segment Routing is promising with rapid technological advancements and increasing industry adoption. This innovative network routing technique continues to evolve, offering more efficient ways to manage data flows across complex networks.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in Segment Routing are shaping the future of networking. These innovations enhance network efficiency and simplify operations.
- SRv6 (Segment Routing over IPv6): SRv6 extends Segment Routing capabilities over IPv6, allowing for more scalable and flexible networks.
- Automation and Orchestration: Automated tools and orchestration platforms are making Segment Routing easier to deploy and manage.
- Enhanced Security: New security features are being integrated into Segment Routing to protect data flows.
- Improved Network Performance: Segment Routing optimizes network paths, reducing latency and improving performance.
Industry Adoption
Industry adoption of Segment Routing is growing rapidly. Many companies recognize its benefits and are integrating it into their networks.
| Industry | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Improved network efficiency and scalability. |
| Cloud Providers | Better data flow management and reduced latency. |
| Enterprises | Enhanced network security and simplified operations. |
Segment Routing’s flexibility and efficiency make it a valuable asset across various industries.
Credit: rayka-co.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Segment Routing Vs Mpls?
Segment routing simplifies network paths by encoding them into packet headers. MPLS uses labels for path determination. Segment routing offers more flexibility and scalability compared to MPLS. Both enhance network efficiency but differ in implementation and management.
What Is Segment Routing And Bgp?
Segment routing simplifies network traffic management using source-based routing. BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) handles routing between different networks on the internet. Both enhance network efficiency and reliability.
What Is The Advantage Of Segment Routing?
Segment routing improves network efficiency. It reduces latency and simplifies traffic management. It enhances scalability and flexibility.
How Is Segment Routing Different From Traditional Routing?
Segment routing differs by allowing packets to follow predetermined paths, enhancing network efficiency and flexibility.
Conclusion
Segment Routing offers significant benefits for network efficiency and scalability. Its simplified architecture enhances performance and reduces costs. By adopting Segment Routing, organizations can future-proof their networks. Embracing this technology ensures better traffic management and improved user experiences. Stay ahead in the networking field by leveraging the advantages of Segment Routing today.