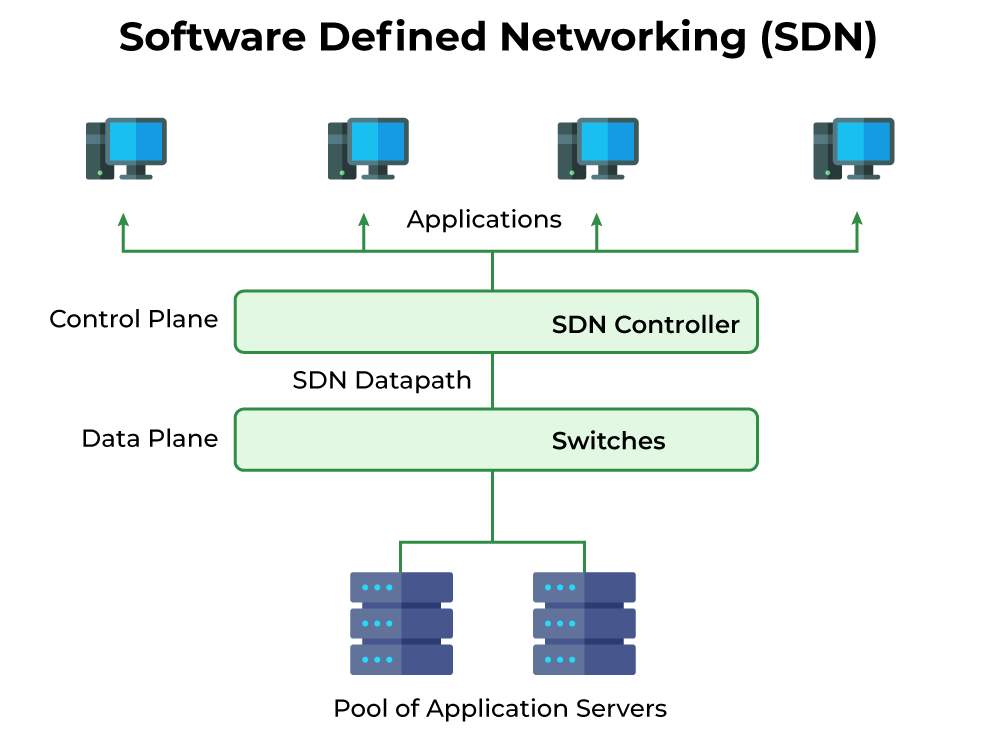
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) separates the control plane from the data plane in network architecture. This allows centralized management and dynamic configuration of network resources.
SDN offers significant flexibility and efficiency in managing complex networks. It provides a centralized control point, which simplifies network management and improves scalability. Network operators can quickly adapt to changing demands and optimize performance. SDN also enhances security by allowing administrators to implement policies consistently across the network.
This approach reduces hardware dependency and lowers operational costs. Businesses benefit from increased agility, enabling faster deployment of new services. Overall, SDN revolutionizes traditional networking, making it more responsive and easier to manage. This technology is essential for modern, dynamic network environments.
Core Components
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is revolutionizing network management. Its core components are pivotal. These components ensure flexibility, efficiency, and centralized control. Let’s delve into the essential parts of SDN.
Controllers
The Controller is the brain of SDN. It manages all network traffic. Controllers make decisions based on the network’s needs. They centralize control, making it easier to manage. Controllers also communicate with both the data and application planes.
Data Plane
The Data Plane handles the actual data packets. It forwards data to the correct destination. The Data Plane relies on instructions from the Controller. It ensures data flows smoothly across the network. Speed and efficiency are crucial here.
Application Plane
The Application Plane hosts network applications. These applications can be firewalls, load balancers, or monitoring tools. The Application Plane interacts with the Controller for real-time updates. This makes network management more dynamic and responsive.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Controller | Centralizes network control and decision-making |
| Data Plane | Handles and forwards data packets |
| Application Plane | Hosts and runs network applications |
Understanding these core components is key. They are the backbone of Software-Defined Networking. Each component plays a vital role in network efficiency and flexibility.
Benefits Of Sdn
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) offers a modern approach to network management. It separates the control plane from the data plane, enabling smarter and more efficient networks. Explore the key benefits of SDN below.
Flexibility
SDN provides unparalleled flexibility in network management. Administrators can quickly change network configurations through software, without touching physical devices. This adaptability allows for rapid deployment of new applications and services.
With SDN, networks can be easily programmed to meet specific needs. This ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and effectively. It also allows for better traffic management and optimization.
Scalability
SDN is designed to be highly scalable. Whether you are managing a small business network or a large data center, SDN can handle it. The centralized control plane simplifies the management of multiple devices and locations.
As your network grows, SDN makes it easy to add more devices and services. This scalability ensures that your network can grow with your business. It reduces the complexity and cost of network expansion.
Cost Efficiency
One of the key benefits of SDN is its cost efficiency. Traditional networks often require expensive hardware upgrades. With SDN, software updates can achieve the same goals at a lower cost.
SDN also reduces operational costs. Centralized management means fewer resources are needed to maintain the network. This results in lower labor costs and less downtime.
In summary, SDN offers flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. These benefits make it an attractive option for modern network management.
Sdn In Cloud Computing
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) revolutionizes Cloud Computing by enhancing network flexibility and efficiency.
Integration With Cloud
SDN seamlessly integrates with cloud platforms, enabling dynamic network configuration.
Enhanced Resource Management
SDN optimizes resource allocation in the cloud, boosting performance and scalability.

Credit: www.sdxcentral.com
Security Enhancements
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) brings significant security enhancements to modern networks. It offers centralized control and programmability, which improves security.
Improved Network Security
SDN provides a centralized view of the entire network. This helps in applying consistent security policies. Administrators can quickly implement firewall rules and access controls across all devices.
- Centralized Control: Simplifies security management.
- Consistent Policies: Uniform security policies across the network.
- Dynamic Response: Quickly adapt to new threats.
SDN allows for dynamic network segmentation. This limits the movement of threats within the network. It isolates infected segments, stopping the spread of malware.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Centralized Control | Streamlined security management |
| Dynamic Network Segmentation | Limits threat movement |
| Consistent Policies | Uniform security enforcement |
Threat Detection
SDN improves threat detection with real-time monitoring. It quickly identifies unusual activities. This helps in early threat detection.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Detects threats instantly.
- Behavior Analysis: Identifies abnormal patterns.
- Automated Alerts: Immediate notification of threats.
SDN uses machine learning for threat detection. It learns from past incidents. It predicts and mitigates potential threats.
Automated responses help in quick threat mitigation. The system can isolate affected devices. This prevents further damage.
Challenges And Limitations
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) brings many benefits, but it also has challenges and limitations. These issues can impact the efficiency and adoption of SDN.
Technical Challenges
SDN faces several technical challenges that can hinder its performance.
- Scalability: Managing large networks can be complex.
- Latency: Network delays can affect performance.
- Security: SDN introduces new vulnerabilities.
These challenges require advanced solutions to ensure smooth operation.
Adoption Barriers
Adopting SDN is not always easy. There are several barriers:
- Cost: Initial setup can be expensive.
- Complexity: SDN needs skilled personnel.
- Compatibility: Integrating with existing systems can be tough.
Organizations must consider these factors before implementing SDN.
| Technical Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Managing large networks can be complex. |
| Latency | Network delays can affect performance. |
| Security | SDN introduces new vulnerabilities. |
Addressing these challenges and barriers is crucial for SDN success. Organizations need to plan carefully and invest in solutions that mitigate these issues.

Credit: community.fs.com
Future Trends
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is changing the way networks are managed. The future trends in SDN are promising and exciting. Let’s explore the key trends that will shape the future of SDN.
Ai And Sdn
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a crucial role in SDN. AI can automate network management tasks. This reduces human errors and improves efficiency. AI algorithms can predict network issues before they happen. This leads to better network reliability.
Machine learning helps in optimizing network performance. It analyzes data to make smart decisions. AI in SDN can also enhance security. It can detect and respond to threats in real-time.
Here are some key benefits of AI in SDN:
- Automation of network tasks
- Predictive maintenance
- Enhanced security
- Improved network performance
Edge Computing
Edge Computing is another trend impacting SDN. It brings data processing closer to the source. This reduces latency and improves response times. Edge computing works well with SDN to manage distributed networks.
With edge computing, data doesn’t need to travel to a central server. This speeds up data processing. It also saves bandwidth. SDN can manage edge devices efficiently. This ensures smooth operation of the entire network.
Benefits of Edge Computing in SDN include:
- Reduced latency
- Faster data processing
- Bandwidth savings
- Efficient management of edge devices
As we look ahead, the combination of AI and Edge Computing will drive SDN forward. These technologies will make networks smarter and more efficient. They will redefine the way we think about network management.
Real-world Applications
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is transforming how networks operate. SDN allows centralized management of network resources. This opens up various real-world applications. Here, we explore some compelling use cases.
Case Studies
Google uses SDN for efficient traffic management. Their B4 network links data centers worldwide. SDN optimizes data flow and reduces congestion.
Microsoft employs SDN to support its Azure platform. SDN helps balance workloads. This ensures seamless cloud services for users.
Industry Use Cases
Healthcare benefits greatly from SDN. SDN enables secure, fast data transfer. This is crucial for patient records and telemedicine.
Education institutions use SDN for flexible network management. SDN allows quick adaptation to changing needs. Schools can easily manage online learning platforms.
Retail leverages SDN to enhance customer experience. SDN provides reliable and speedy network connections. This is vital for point-of-sale systems and inventory management.
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Data Transfer | Secure, fast patient records |
| Education | Network Management | Adaptable online learning |
| Retail | Customer Experience | Reliable POS systems |
SDN is reshaping various industries. Its applications are wide-ranging and impactful.

Credit: avinetworks.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Software Defined Networking?
Software Defined Networking (SDN) centralizes network control by separating the control plane from the data plane. This enables dynamic, efficient network management through software applications. SDN improves network performance, flexibility, and scalability, making it ideal for modern, complex network environments.
What Is An Example Of Sdn?
An example of SDN is OpenFlow. It allows network controllers to determine the path of network packets.
What Is Sdn In Layman’s Terms?
SDN, or Software-Defined Networking, is a technology that makes networks more flexible and easier to manage using software.
What Are Two Characteristics Of Software-defined Networking?
Software-defined networking features centralized control and programmability. It separates the control plane from the data plane.
Conclusion
Software-Defined Networking is transforming how networks are managed and operated. Its flexibility and efficiency are game-changers. Adopting SDN can significantly boost your network’s performance. As technology evolves, staying informed about SDN advancements is crucial. Embrace SDN to future-proof your network and stay competitive in the digital landscape.